The AER exists to ensure consumers are better off now and in the future
Consumers are at the heart of everything we do.
The AER works to ensure energy consumers have access to a reliable and secure market and that they pay no more than necessary for energy to their homes and businesses.
We do this by setting the maximum amount of revenue that monopoly electricity networks and natural gas pipelines can earn from consumers.
We monitor network, wholesale and retail market performance and compliance with national energy legislation. We take enforcement action when there is potential or actual harm to consumers.
We set the Default Market Offer which is a price cap on standing energy contracts and we provide a price comparison website, Energy Made Easy, so consumers can find the best energy contract for them.
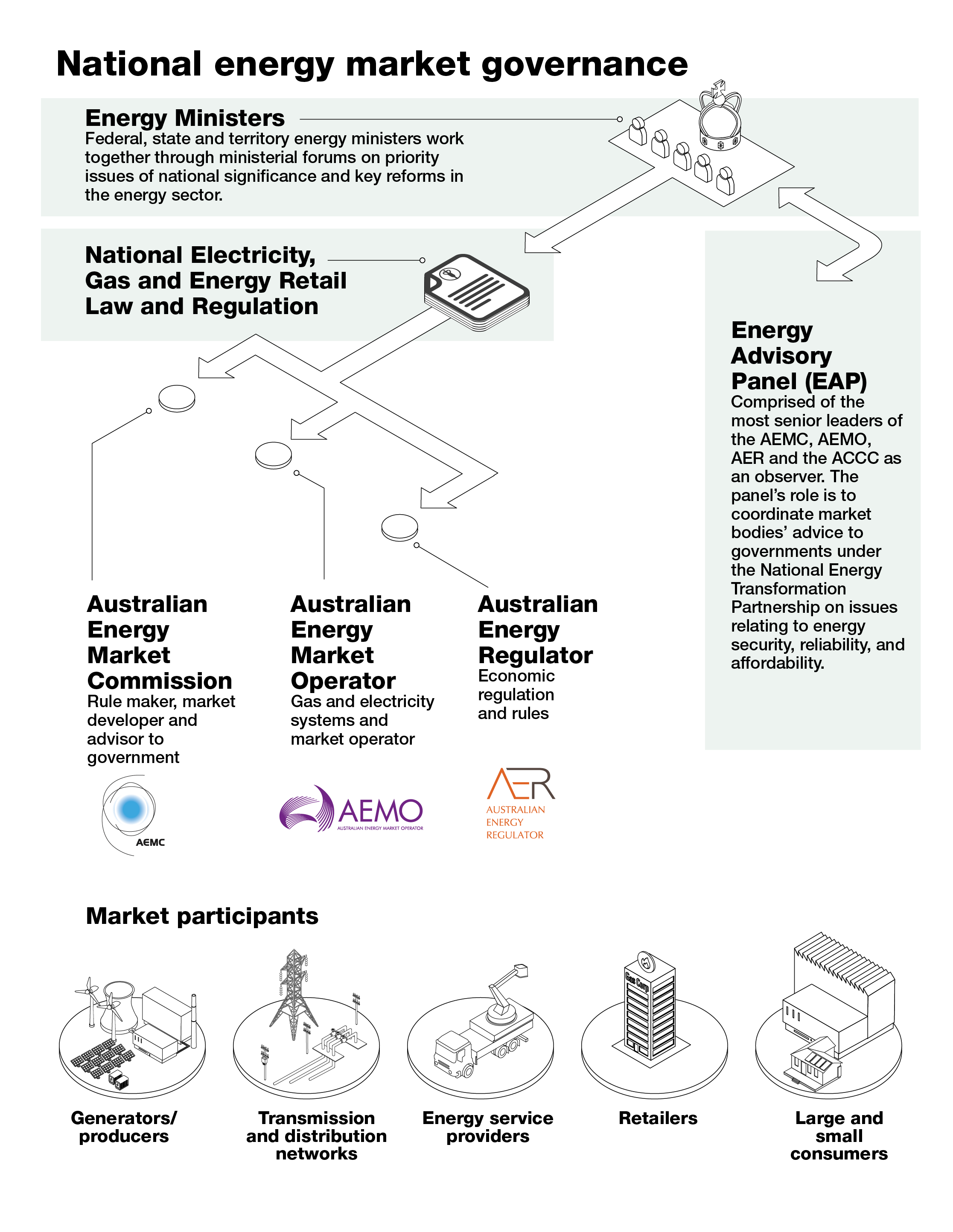
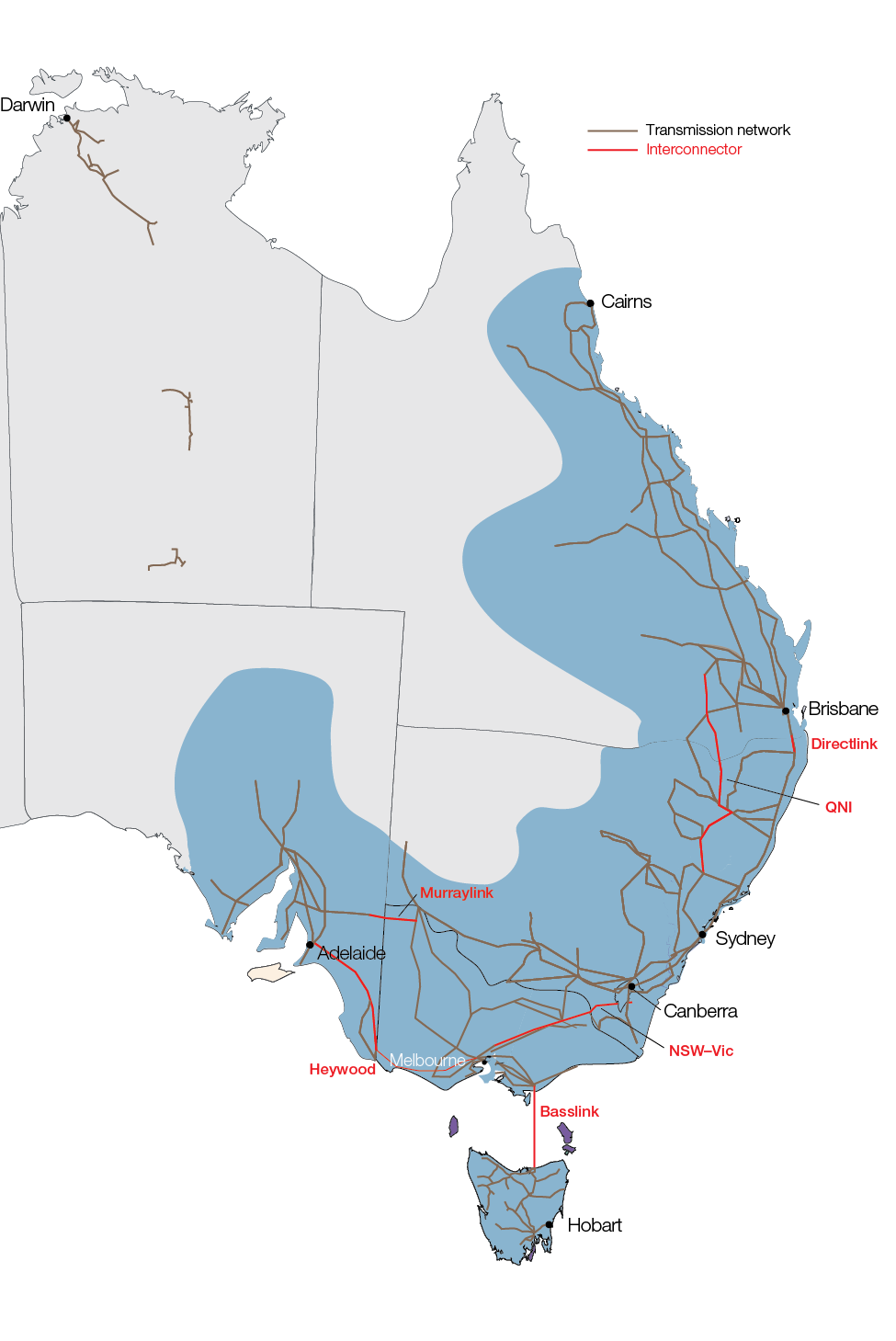
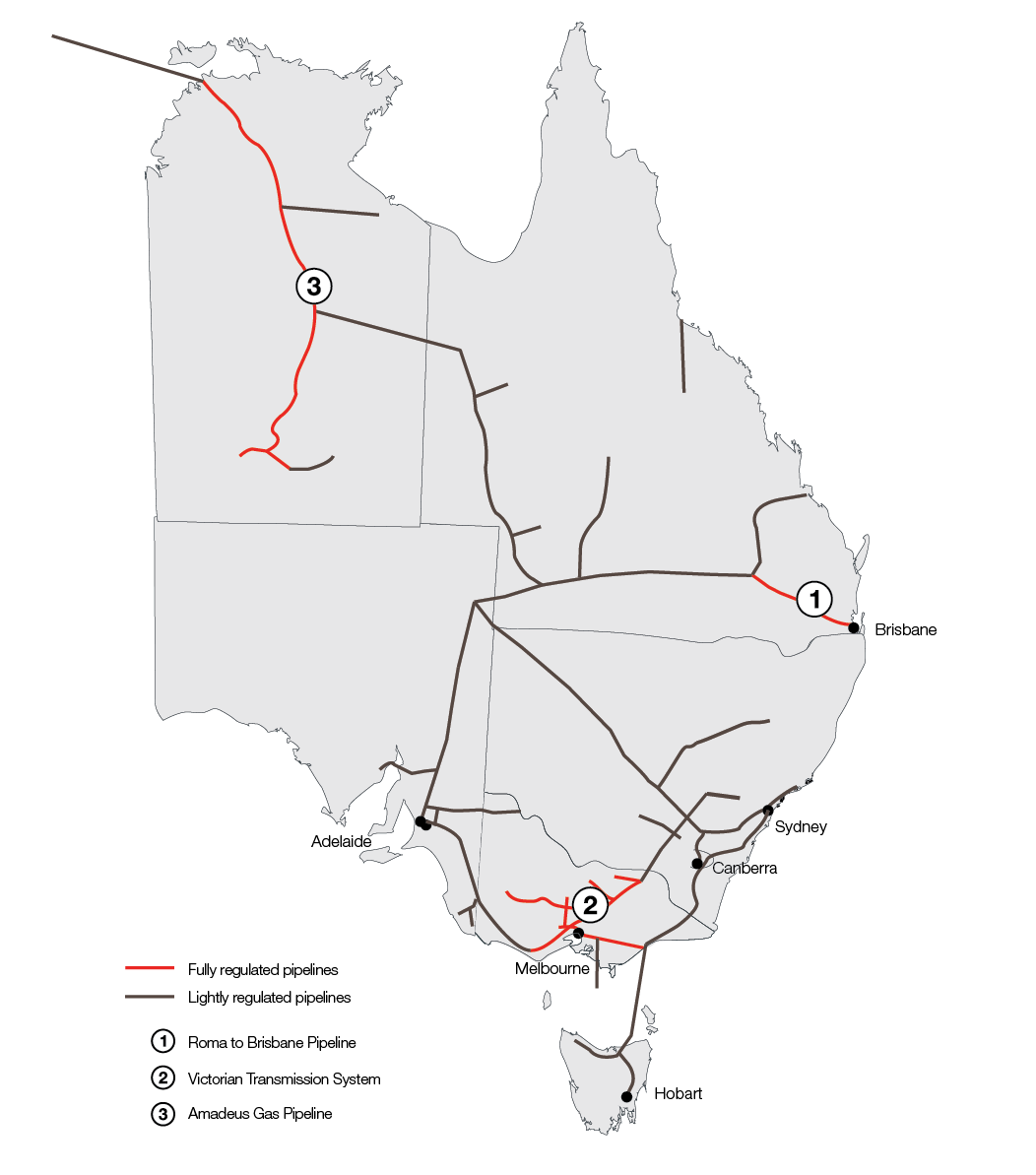
Where we fit in Australia's energy system
The AER is one of 3 major market bodies that oversee national electricity and gas markets in Australia.
- The Australian Energy Market Commission (AEMC) develops the rules by which the markets must operate.
- The Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO) manages the day-to-day operations of the markets.
- The Australian Energy Regulator (AER) monitors performance and compliance with the rules.
Collectively, the AEMC, AEMO and the AER support the Energy and Climate Change Ministerial Council in its role to develop and coordinate national energy policy.
While the market bodies work closely together, each is an independent decision-maker with clear functions, accountabilities and powers.